Blockchain Signer Integrity Explained
Blockchain Signer Integrity
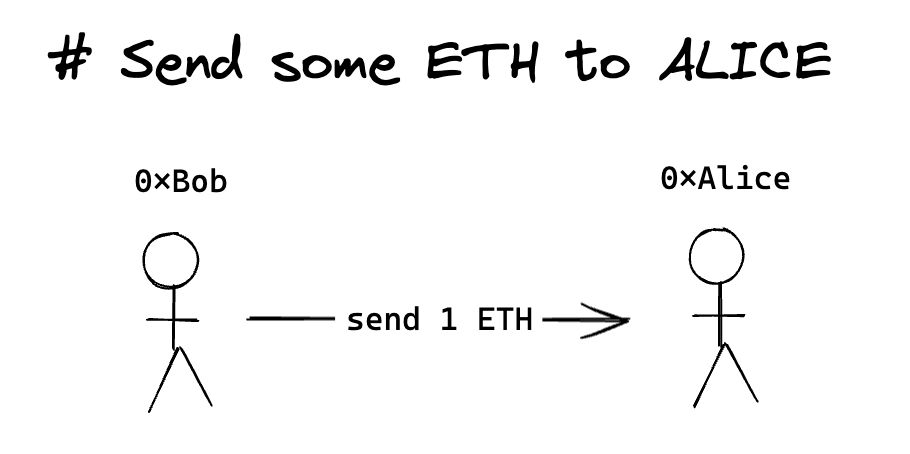
Happy Tuesday everyone! Today, we’re diving into a critical aspect of blockchain technology: signer integrity. This concept is key to understanding how blockchain maintains security and trust. Specifically, when Bob sends crypto to Alice, how does the blockchain verify that the transaction is genuinely from Bob?
The Role of a Wallet in Blockchain
In the blockchain realm, a wallet is more than just a place to store digital currency; it’s your identity and access key rolled into one. This wallet is composed of two parts: a private key and a public key, which together generate a unique blockchain address.
Key Generation
When someone like Bob sets up his blockchain wallet, it starts with the creation of a private key. This key is essentially a random but unique set of numbers and letters. From this private key, a corresponding public key and blockchain address are derived.
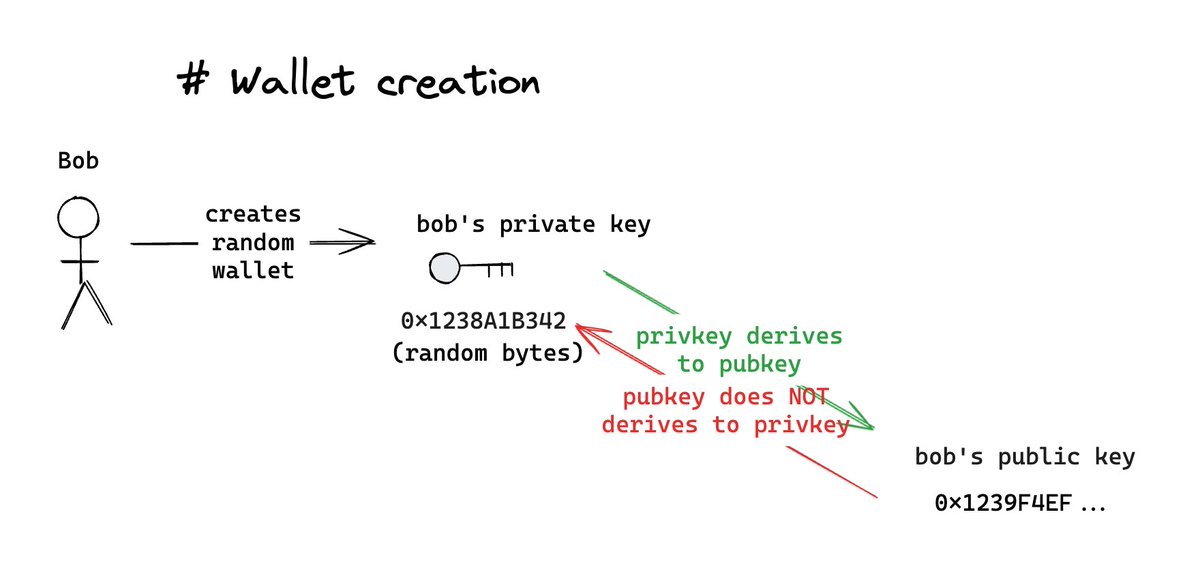
Bob’s private key is his secret tool for approving transactions. The public key and address, however, are visible on the blockchain for transparency and verification.
Securing the private key is critical. If it’s compromised, it’s equivalent to giving someone the key to your bank vault 🚨.
Transaction Signing: A Closer Look
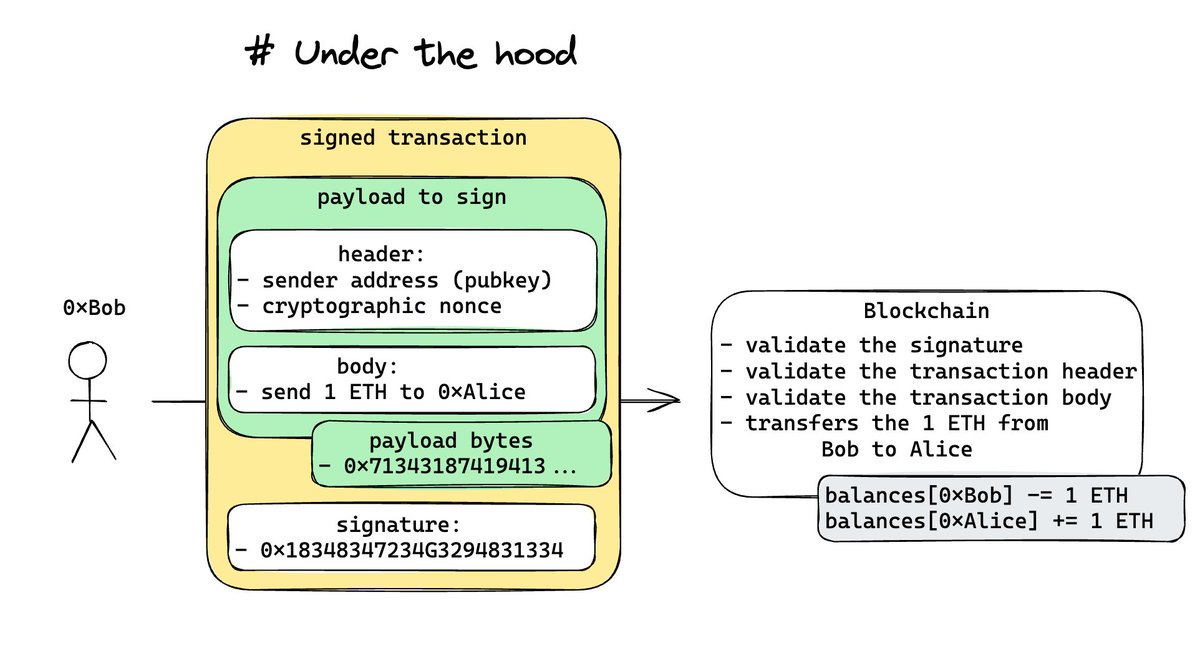
Imagine Bob wants to send 1 ETH to Alice. His wallet facilitates this by signing the transaction.
The Signature Process
Bob’s wallet uses his private key to sign the transaction, which includes the transaction details, such as sending 1 ETH to Alice.
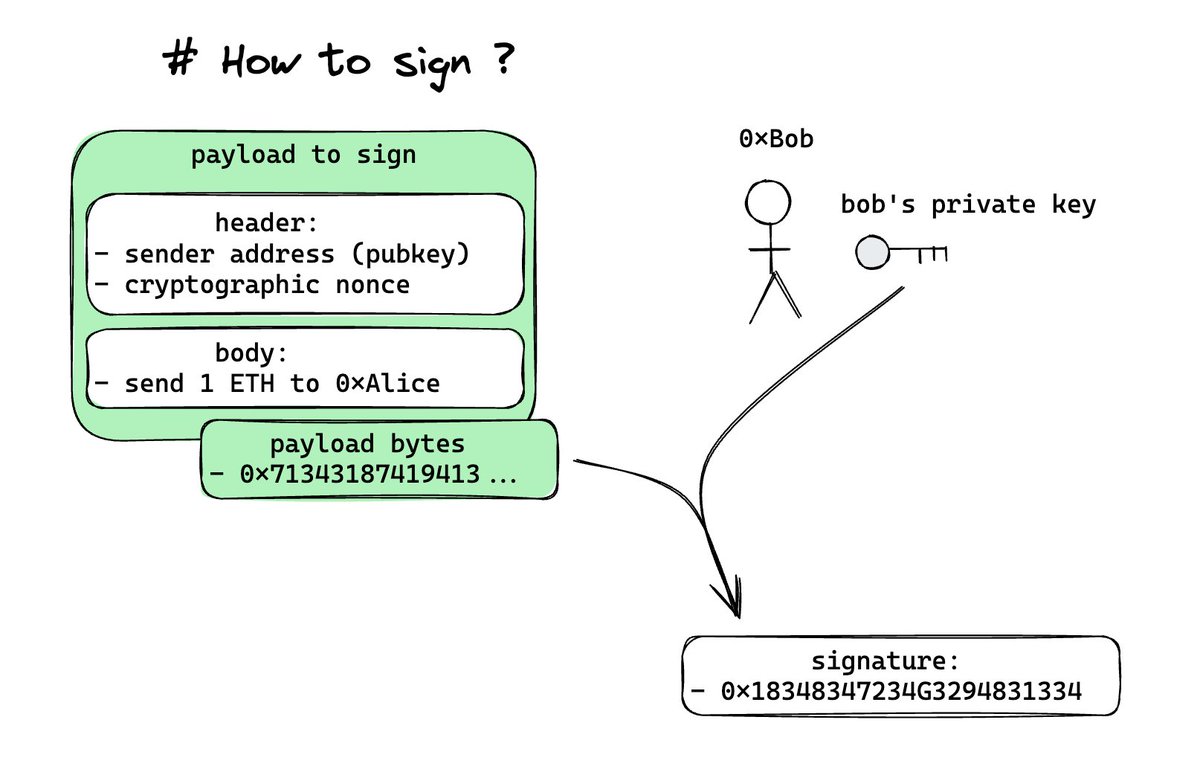
This data is encoded into bytes and signed using a signature function. This signature serves as proof that Bob initiated the transaction and that the details remain unaltered.
Verifying Transaction Authenticity
The receiving end, in this case, the blockchain, needs to verify that the message was indeed signed by the sender of the funds (Bob).
Given the signature and the payload, a cryptographic function can recover the public key of the signer. It then checks if the signer’s public key matches Bob’s public key.
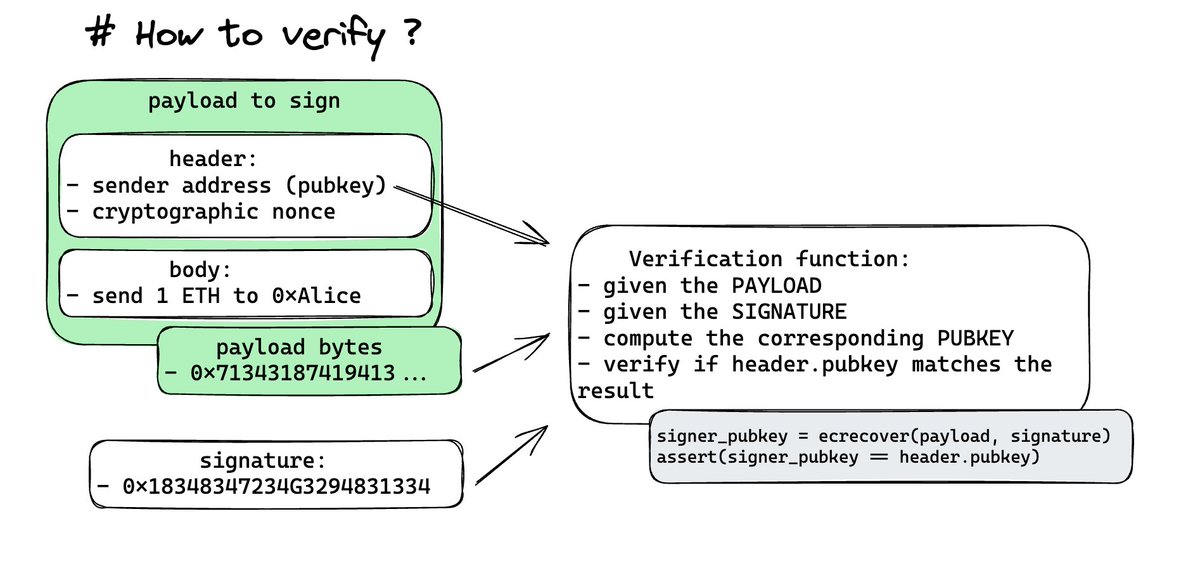
This verification is a fundamental step in confirming Bob’s identity as the sender.
Key Takeaways
- Transactions on the blockchain are not direct transfers but are processed and verified by the network.
- Signing transactions is an essential process, establishing the authenticity and integrity of the information.
- Blockchain technology ensures that every transaction is thoroughly verified before being executed.
I hope this helps in understanding how transactions are handled in the crypto world! 🌐